SHA-256 Rollout
Feb 25, 2026
Background
SHA-2 consists of a family of cryptographic hashing algorithms developed in part by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) to replace the aging SHA-1 hashing algorithm which may have mathematical weaknesses.
GlobalSign, in our role as your security partner, supported the deprecation of SHA-1 and the transition to SHA-256, the most widely supported hashing algorithm within the SHA-2 family.
This article defines the important milestones for the introduction of SHA-256 Certificates and the depreciation of SHA-1 Certificates.
Important dates for SHA-1 deprecation:
As of January 16, 2015, CAs will be forbidden to issue SHA-1 Certificates that expire past December 31, 2016. Microsoft, Google, and Mozilla will start rolling out updates to stop trusting SHA-1 SSL Certificates shortly after 1 January 2017. These browsers will show an untrusted warning message to website visitors.
Microsoft's Timeline:
|
|
|
|---|---|
| January 1, 2016 | Microsoft will cease trusting Code Signing Certificates using SHA-1 |
| January 1, 2017 | Microsoft will cease trusting SSL Certificates using SHA-1 |
| February 14, 2017 | Microsoft will roll out their patches to disable trust to http://aka.ms/sha1 |
Google's Timeline:
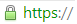
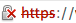
Google's Chrome/Chromium browser will behave differently depending on the version and the expiration date of the SSL Certificate. Note that SHA-1 SSL Certificates that are valid past 1/1/2017 will show as untrusted in Chromium 41. Based on past release cycles, we expect Chrome 41 to be available 10 February 2015. Google is planning to remove support for SHA-1 Certificates in Chrome 56, which will be released to the stable channel around end of January 2017.
|
|
Nov 18, 2014 |
Dec 30, 2014 |
Feb 10, 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|
| After January 1, 2016 |
 |
 |
 |
| After June 06, 2016 |
 |
 |
 |
| After January 01, 2017 |
 |
 |
 |
| Date | Action |
|---|---|
| January 31, 2017 | Google will remove support for SHA-1 Certificates in Chrome 56 |
| January 1, 2019 | Enable SHA-1 For Local Anchors Policy will be removed in the first Chrome release |
Mozilla's Timeline
Mozilla's timeline is also based primarily around Certificate expiration dates and is more in line with Microsoft's timeline. Note that after January 01, 2017, Firefox will not trust any SHA-1 Certificate. Also, Firefox 51 will be released to enable the deprecation of SHA-1 SSL Certificates.
The warnings in the chart below will begin appearing in Firefox versions released in early 2015.
|
|
|
|---|---|
| Issued After January 1, 2016 | "Untrusted Connection" |
| Expires After January 01, 2017 | Warning displayed. |
Related Articles
SSL Configuration Test
Check your certificate installation for SSL issues and vulnerabilities.
