AEG: How to Check the Functional Levels in Active Directory
Dec 8, 2022
AEG: How to Check the Functional Levels in Active Directory
Introduction
AEG leverages both Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) and Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) capabilities. In this sense, functional levels determine the available AD DS domain and forest capabilities. AD DS and AD CS work together, and some features such as the Certificate Enrollment Web Services and the Cross-forest Enrollment require the following
- AEG requires that the forest functional level must be Windows Server 2008 R2 or higher.
- The domain functional level must be the same or higher than the forest functional level.
- You can set the domain functional level to a value that is higher than the forest functional level, but you cannot set the domain functional level to a value that is lower than the forest functional level.
- If your environment has more than one forest, the forests must also include a two-way trust relationship to support cross-forest enrollment.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Functional Level supports the following Windows Server versions:
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2019
Guidelines
There are three ways to verify your current forest and domain functional levels on your Active Directory Domain Controller. You can use the Server Manager, the Administrative Tools, or the PowerShell. In this article, we show you the steps to use any of those tools.
Using the Server Manager
-
Log in to your Active Directory Domain Controller. Note: If you have more than one domain controller, you should log in to the forest root domain controller.
-
Open the Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Active Directory Domains and Trusts as shown in the diagram below.
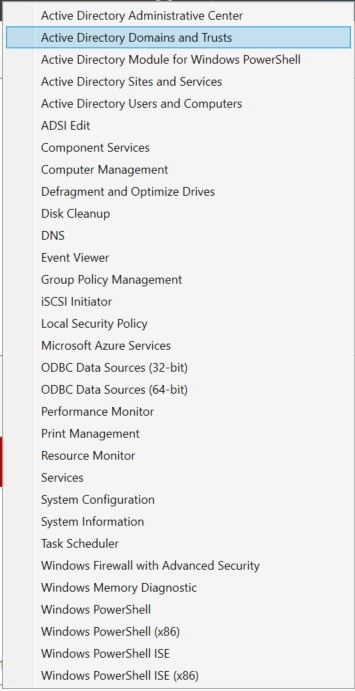
-
Right-click the root domain, and click Properties to proceed.
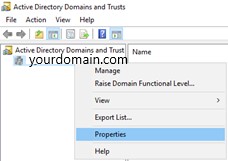
-
Under the General tab, you will find the forest and domain functional levels currently configured on your Active Directory Domain Controller.
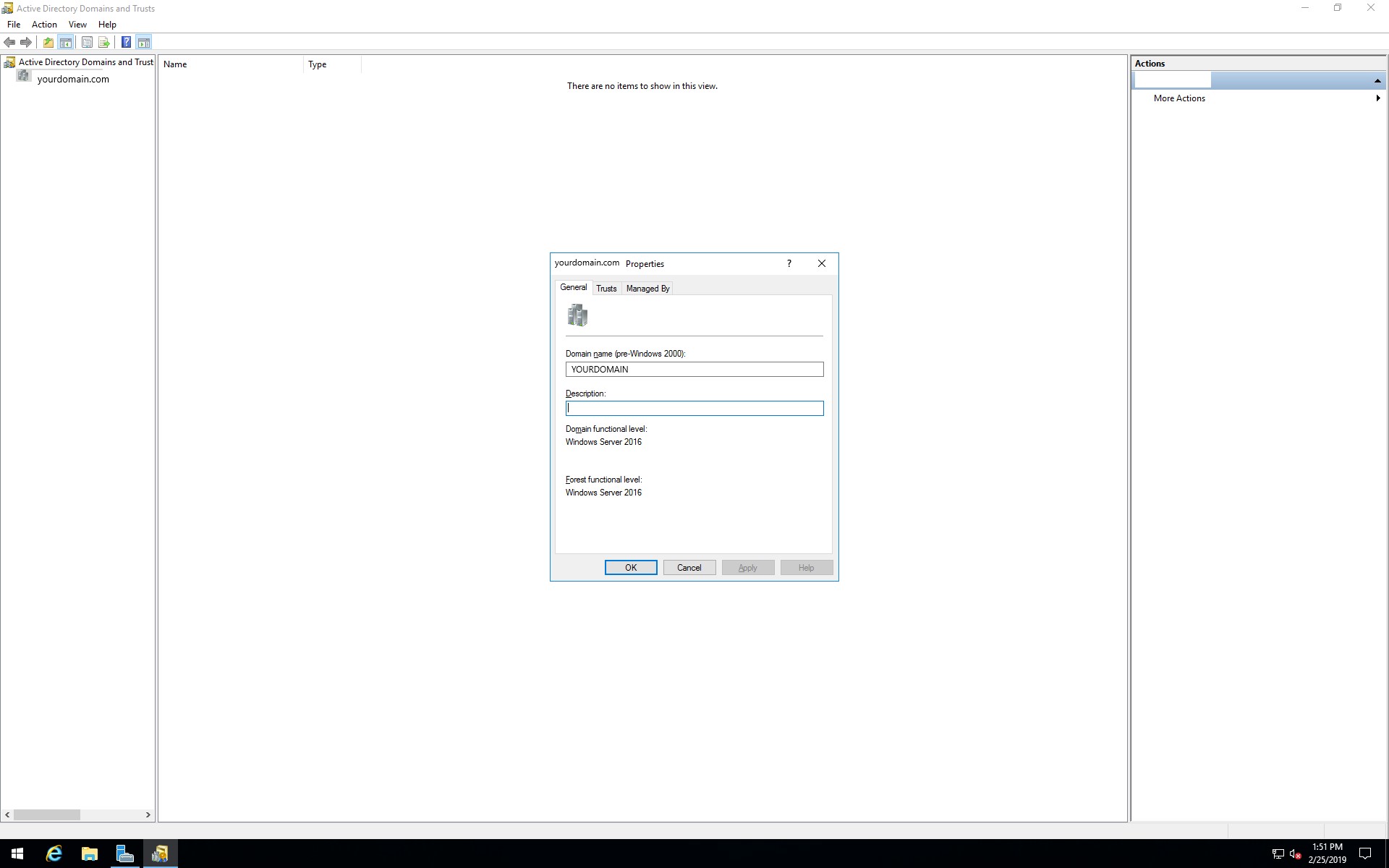
Using the Administrative Tools
-
Log in to your Active Directory Domain Controller. Note: If you have more than one domain controller, you should log in to the forest root domain controller.
-
Click the Start Menu, and click Windows Administrative Tools.
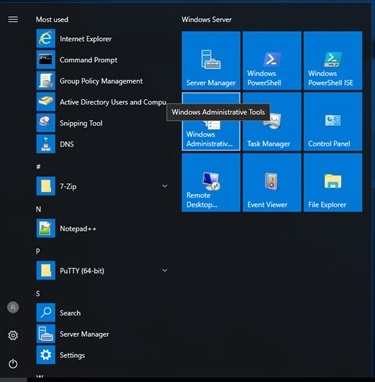
-
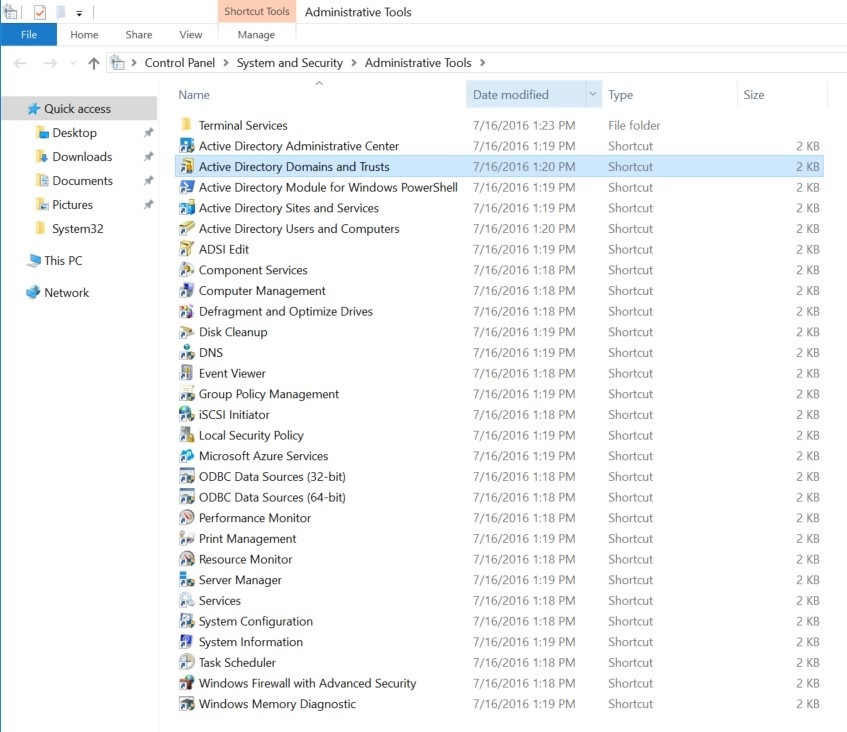
Find Active Directory Domains and Trusts on the list, and double click on it.
-
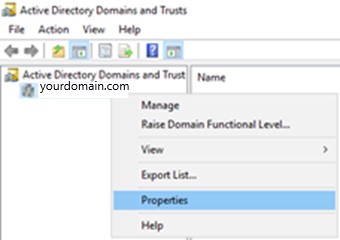
Right-click the root domain, and click Properties.
-
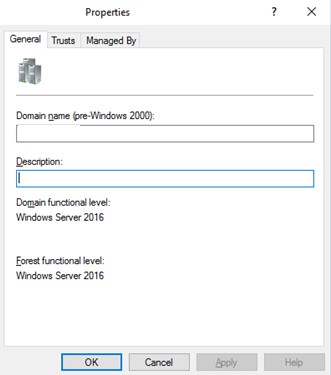
Under the General tab, you will find the forest and domain functional levels currently configured on your Active Directory Domain Controller.
Using the PowerShell
-
Log in to your Active Directory Domain Controller. Note: If you have more than one domain controller, you should log in to the forest root domain controller.
-
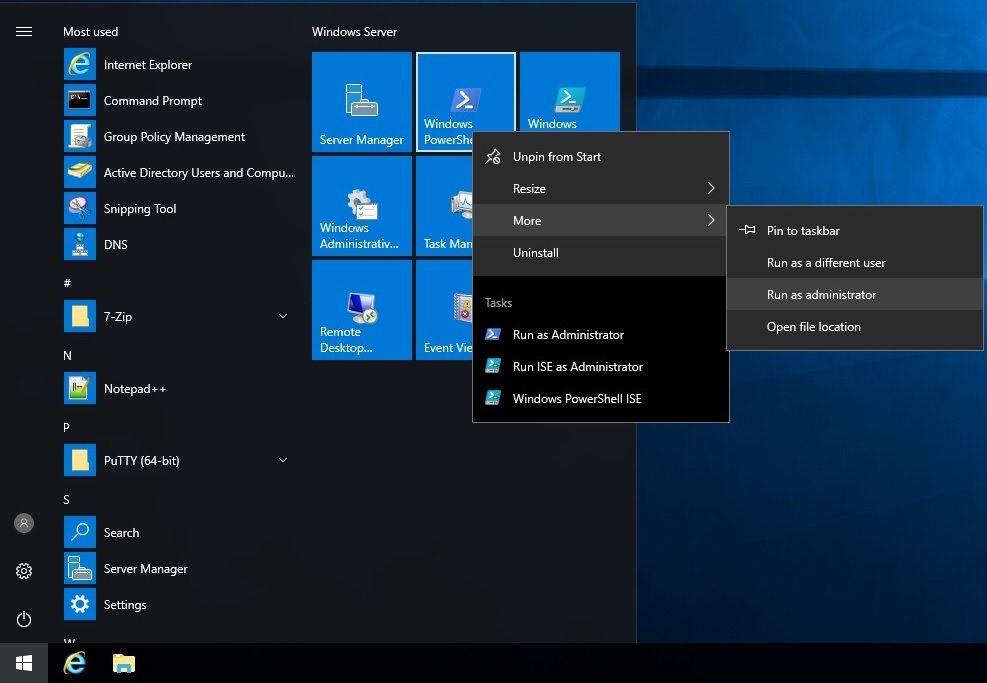
Click the Start Menu, and click Windows PowerShell. Hover over More, and click Run as administrator to proceed.
-
If there is a pop-up screen from the User Account Control, or UAC, asking if you want to allow the app to make changes, click Yes.
-
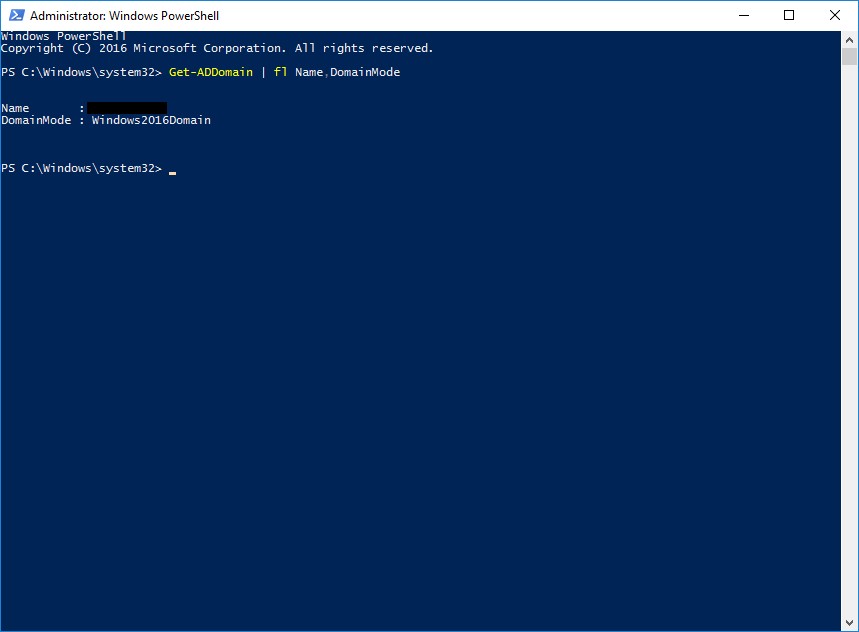
To find the Domain Functional Level, use the command "Get-ADDomain | fl Name,DomainMode”.
-
To find the Forest Functional Level, use the command “Get-ADForest | fl Name,ForestMode”.

After following the previous steps, you will have a clear idea on what Domain and Forest Functional Levels your environment is running on. If your environment does not support the Windows Server 2008 R2 functional level, you should plan on how to upgrade your infrastructure before deploying AEG.
Related Articles
SSL Configuration Test
Check your certificate installation for SSL issues and vulnerabilities.
